Conductivity of RO Water (Typical Range + Limit)
Written by: Gene Fitzgerald // Last Updated: Jun 28, 2023
This page may contain affiliate links. If you buy a product or service through such a link we earn a commission at no extra cost to you. Learn more.
While not many people put much thought into this, the conductivity of reverse osmosis water is actually different from that of regular water.
This should make sense if you know how reverse osmosis works and what conductivity is in the first place.
After all, water conductivity is mainly dictated by the presence of various impurities, pretty much all of which get removed by reverse osmosis…
Key Takeaways
- The conductivity of reverse osmosis water is around 0.05 to 15 µS/cm.
- Water filtered with a reverse osmosis system for home use usually has 5 to 15 µS/cm.
What Is the Conductivity of RO Water?
So, what is the conductivity of RO water? RO water has a conductivity of anywhere between 0.05 and 15 µS/cm. Water filtered with a regular reverse osmosis system usually ranges between 5 and 15 µS/cm.
The conductivity of water is measured in microsiemens per centimeter (µS/cm) or micromho per centimeter (μʊ/cm). Alternatively, you can measure the inverse, the resistivity, which is measured in megohm-centimeter (MΩ-cm).
Pure water without any contaminants in it, which is pretty much what very clean reverse osmosis water is, should have a conductivity of 0.05 and a resistivity of around 18 MΩ-cm.
What Is Water Conductivity Anyway?
Conductivity is a measure of how well water conducts electricity. The higher the conductivity is, the better electric current can pass through the water.
What Affects Water Conductivity?
The conductivity of water is mainly dictated by the presence of different types of impurities. Some impurities increase water conductivity, while others decrease it. Various inorganic compounds like chloride, nitrate, and sulfate can increase the conductivity of water. On the other hand, organic compounds like phenol, oil, and alcohol decrease the conductivity of water.
The temperature of water also plays a role when it comes to conductivity, with warmer water being a better conductor. This makes it important to take measurements at a consistent temperature if you’re trying to determine the conductivity of your reverse osmosis water. Usually, 25 °C which equals 77 °F is used as a standard baseline.
Conductivity vs. TDS
Conductivity should not be confused with TDS, which is a general measurement for dissolved solids in water.
However, a TDS factor can be used to calculate the total dissolved solids in water from a conductivity measurement – and vice versa. The factor will depend on what types of solids are dissolved in the water and can be adjusted accordingly. For reverse osmosis water, you are probably looking at a factor of around 0.4 to 0.5.
For example, if you have a water conductivity of 10 µS/cm and a conversion factor of 0.4, then you get a TDS of 10 x 0.4 = 4.
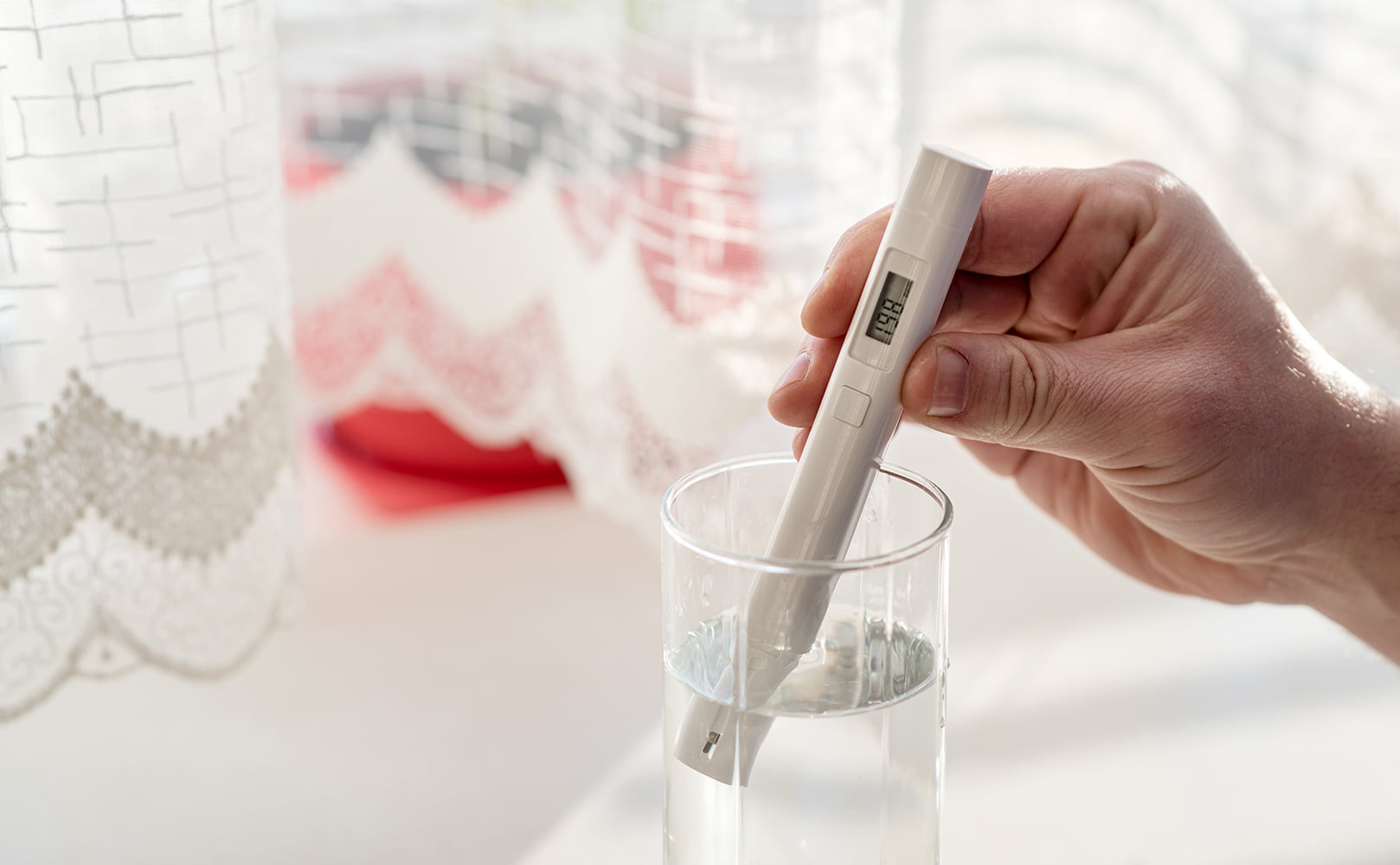
How Can I Measure the Conductivity of My Reverse Osmosis Water?
You can measure the conductivity of reverse osmosis water by taking a sample of it and using a special meter. You immerse the meter’s two electrodes in your water sample and run electricity between them. The device measures the decrease in voltage along the path. In other words, it measures the resistance of the water. Then, the meter calculates the conductivity based on that and gives you the end result.
Another way would be to measure RO water TDS and then calculate the conductivity using the conversion factor. But again, in this case you would have to know what leftover impurities you have in your water. The formula goes like this: TDS / Factor = Conductivity
By the way, this is also exactly how TDS meters work. They measure the conductivity of a solution and then estimate TDS content based on that reading. This also shows that TDS meters are not 100% precise – they always use the same factor regardless of the types of dissolved solids in your water.
Why Could RO Water Conductivity Be Important to Monitor?
Most people don’t care about the conductivity of their reverse osmosis water and never bother to measure it. However, this can be a useful indicator of how well your reverse osmosis system is working in general. By measuring the conductivity of your reverse osmosis water, you can figure out how much TDS gets rejected by the membrane. More TDS in your water means that the membrane is likely not working as optimally as it should. This can be detected by the higher conductivity of the water.
Membrane Integrity
An increase in conductivity can indicate the need to replace your reverse osmosis membrane. Keep in mind that you should probably not rely on this as a sole indicator for any issues, but you should still pay attention to it if you have access to the equipment to measure it. You should generally not have to replace your RO membrane more often than once every couple of years, but there might be some exceptional cases that require more frequent maintenance.
Why Do I Have High RO Water Conductivity and How Can I Reduce It?
If your reverse osmosis water has a high conductivity, this is probably a bad sign and indicates that you need to fix something. In most cases, the fix might be as simple as changing the reverse osmosis membrane. You should also look for leaks along the system. Pay special attention to the brine seals and the inner connector seals. A brine leak can easily increase the conductivity of your reverse osmosis water.
Other RO Permeate Water Parameters You Can Monitor
If you want to get a good idea of how well your reverse osmosis system is working and whether there are any potential issues to watch out for, there are several other parameters that you can monitor.
Temperature
Pay attention to the temperature of your water. Reverse osmosis systems are usually rated for a very specific temperature, typically 77 °F. Higher and lower temperatures can have various effects on the operation of your reverse osmosis system. Typically, higher temperature increases the flow rate of water but at the same time lowers the RO membrane’s salt rejection rate; while lower water temperature decreases flow but increases salt rejection. You should therefore monitor your temperature and try to maintain it at a consistent level.
Flow
Look at the flow rate of your water as well. If it gets too low, this probably indicates that your reverse osmosis membrane has gotten clogged. Reverse osmosis always restricts the flow rate of water by default, but there are some reasonable limits to this. If you notice that water is flowing much more slowly than usual, this likely indicates an issue that needs to be addressed.
Pressure
Reverse osmosis relies on a high level of pressure for its operation. If the pressure across the system drops too much, this could decrease the performance of your RO unit. Therefore, it’s a good idea to pay attention to overall pressure levels and make adjustments if you see them dropping too much. Low pressure usually indicates problems with the RO membrane itself and could point to the need for a replacement.
If you have any questions about RO water conductivity please don’t hesitate to leave a comment below!
Information provided on BOS is for educational purposes only. The products and services we review may not be right for your individual circumstances.
We adhere to strict editorial guidelines. Rest assured, the opinions expressed have not been provided, reviewed, or otherwise endorsed by our partners – they are unbiased, independent, and the author’s alone. Our licensed experts fact-check all content for accuracy. It is accurate as of the date posted and to the best of our knowledge.