How Effective Is Reverse Osmosis as a Water Filtration Method?
Written by: Gene Fitzgerald // Last Updated: Jul 21, 2023
This page may contain affiliate links. If you buy a product or service through such a link we earn a commission at no extra cost to you. Learn more.
When investing money into any kind of device, you want to make sure it is effective, even more so when investing in something that is supposed to help your health!
A reverse osmosis system is no exception.
So, let’s look at how effective reverse osmosis actually is, plus all the possible advantages and drawbacks.
Key Takeaways
- As a water filtration method, reverse osmosis is extremely effective.
- Reverse osmosis systems for home use remove (heavy) metals, disinfecting chemicals like chlorine and chloramine, sediment, pesticides and other organic compounds, bacteria and other microorganisms, nitrite/nitrate, salts, radiologicals, and more.
- The reverse osmosis process itself is not effective at removing some minute particles, such as specific pesticides like atrazine, organics like benzene, and dissolved gases like carbon dioxide, chlorine, and radon. But some of the other filter stages in a reverse osmosis system usually deals with these.
How Effective Is Reverse Osmosis as a Water Filtration Method?
So, how effective is reverse osmosis as a water filtration method? In a nutshell, reverse osmosis is very effective.
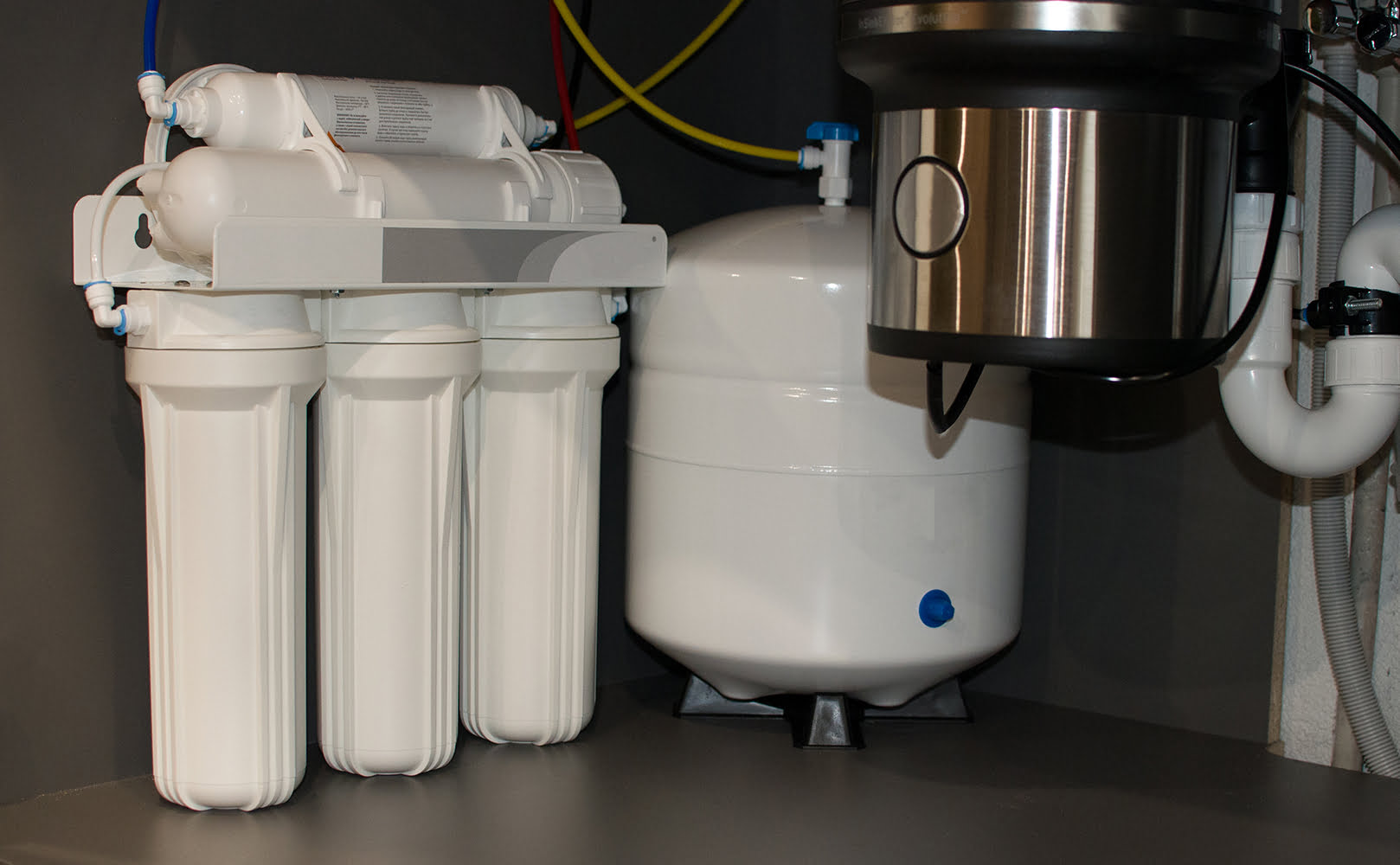
But before we get into the nitty-gritty details, we need to clarify the following: There is a difference between the reverse osmosis water purification process itself and a reverse osmosis system (for home use). That’s because a reverse osmosis system uses more than just an RO membrane to remove contaminants from water; it also uses several pre and post-filters. The most common are sediment pre-filters to remove floating particles and carbon pre/post-filters to remove chlorine, bad taste and odor, gasses, and organic chemicals as a whole.
That said, with its various filter stages, reverse osmosis systems for home use are designed to remove close to all contaminants from water, including metals, salts like nitrate, disinfecting chemicals (chlorine and chloramine), sediments, all sorts of organics, and bacteria and other microorganisms – the reverse osmosis membrane does the bulk of the contaminant removal. This process ensures the water you consume is free from harmful substances, enhancing its safety and taste.
Despite its outstanding effectiveness, reverse osmosis isn’t perfect. It may not eliminate some minute particles such as specific pesticides like atrazine, organic compounds like benzene, and dissolved gases like carbon dioxide, chlorine, and radon. These substances can seep through the RO membrane surface due to their low weight or lack of ionization. However, any impurities not removed by the membrane can typically be filtered out using the additional filters.
What’s more, while reverse osmosis is an excellent solution for purifying water, it’s not the most water-efficient process. It can waste up to 5 gallons of water for every gallon it filters. Good news is, some systems are available that waste considerably less water, and specific methods can help reduce this waste.
What Is Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration and How Does It Work?
Reverse osmosis water filtration is a technique that uses a porous membrane to separate impurities from water. This process involves applying pressure to push the water through this membrane, effectively filtering out undesirable substances. Reverse osmosis can significantly reduce the concentration of contaminants in the water, resulting in cleaner, safer water for consumption or use.
Reverse osmosis is a process that essentially reverses the natural phenomenon of osmosis, which is the migration of water from a less concentrated saline solution to a more concentrated one through a semipermeable membrane. This movement continues until both solutions reach equal concentration. An example of osmosis in real life is a tree’s roots absorbing water from the soil.
What Does RO Remove?
The semipermeable RO membrane, capable of capturing impurities as small as .0001 microns, makes reverse osmosis an effective method for eliminating a wide range of contaminants from tap or well water.
An adequately maintained membrane can effectively remove sediments and other floating particles like asbestos, microorganisms including bacteria, viruses, and cysts, and all kinds of dissolved solids:
- 98% of aluminum and ammonium
- 97% of copper, mercury, nickel, sulfate, sulfite, and zinc
- 96% of arsenic, barium, cadmium, calcium, iron, lead, manganese, and magnesium
- 95% of selenium
- 94% of chromium 6
- 90% of potassium and sodium
- 88% of chloride, cyanide, and fluoride
- 80% of radium
- 68% of nitrates
An RO membrane can also decrease water turbidity by approximately 97.5%.
Remember, these figures pertain to the reverse osmosis membrane alone. A comprehensive reverse osmosis system, complete with pre and post-filters, provides even more thorough protection and can capture a greater range of contaminants.
What Is Not Removed By Reverse Osmosis?
While reverse osmosis is highly effective, some minute contaminants may still seep through: Certain pesticides like atrazine, organic compounds like benzene, and dissolved gases like carbon dioxide, chlorine, and radon. This is mostly owed to their low weight or lack of ionization.
As mentioned before, most impurities not eliminated by the RO membrane will likely be filtered out by the additional filter stages.
The Pros and Cons of Reverse Osmosis Water Treatment
Advantage: Efficient Filtration Ensures Safe Water
Reverse osmosis is one of the best options for comprehensive water purification. It effectively removes virtually all contaminants, making it ideal for highly contaminated and possibly unsafe water. And even when it comes to certain specific water pollutants, there’s no better alternative.
Advantage: Clean Water for Your Culinary Needs
The benefits extend beyond just drinking water. You’ll have a steady source of clean water for cooking, cleaning produce, and dishwashing. The impact on your food can be significant. You might have been grappling with kitchen issues related to polluted water without being aware of it, and switching to RO water can completely change the taste of your dishes.
Advantage: Filtered Water Offers a Pure Taste and Aroma
Water treated with reverse osmosis is as pure as it comes. There won’t be any unusual taste or odor. However, this may not be a plus for some, as only certain contaminants alter the taste and smell of water. If your water doesn’t contain these, you may not notice a change.
Advantage: Ample Supply of RO Water
Reverse osmosis systems may operate at a slower pace, but they make up for this with the storage tank. With a sufficiently sized tank, you’ll always have access to clean water without waiting for the filtration process to complete. Contemporary reverse osmosis systems are equipped with shut-off valves that halt the system when the tank reaches full capacity, eliminating the need to do so manually.
Advantage: Say Goodbye to Plastic Bottled Water
Choosing reverse osmosis can aid in curbing the excessive use of bottled water. While it might be a convenient and sometimes inexpensive option, it has significant drawbacks. Often, the water in these bottles is no different from tap water. Plus, the consumption of bottled water contributes to environmental pollution, an issue that has escalated over the past two decades.
Advantage: Cost-Effective
While there’s an initial cost involved in purchasing and setting up a reverse osmosis system, the long-term savings outweigh this initial outlay. Even for individuals living alone, the system pays for itself in a short time frame. While there are ongoing maintenance costs, they are minor compared to the continual expense of purchasing bottled water on a daily basis.
Advantage: Customizable to Your Needs
One of the key benefits of reverse osmosis systems is their highly customizable nature. You can tailor the pre-filtration stages to match your specific requirements and add components such as UV filtration or a remineralization stage.
Advantage: Energy Efficiency
The operation of a traditional under sink reverse osmosis system relies solely on the water pressure available in your plumbing, making it an energy-efficient solution that does not require electricity.
Advantage: Eliminates Sodium
Water softeners, while beneficial, introduce extra sodium into your water. If this is a concern, a reverse osmosis system can help remove this additional salt. This is especially important for those who already consume a high-sodium diet.
As always, it’s advisable to consult with your doctor before making any significant changes to your diet or water consumption.
Advantage: Achieve Your Daily Water Intake
For some individuals, consistently consuming water requires an extra push. If the water has an unpleasant taste or odor, it can significantly deter you from drinking it regularly. This often leads people to resort to alternatives such as sweetened drinks and other less healthy options. However, with a reverse osmosis system, attaining your daily hydration targets becomes effortless.
Advantage: Clear Ice Cubes
Utilizing reverse osmosis filtration is the ultimate method for creating pristine and transparent ice cubes that will not melt and leave nasty flavors in your drink.
Drawback: Flavorless RO Water
One drawback of having entirely clean water is that it may taste somewhat bland. This is due to the absence of impurities that were previously present in the water. Initially, this might be slightly off-putting, but most people get used to it over time. Eventually, your original tap water might taste unusual, not the purified one.
Drawback: Deprivation of Vital Minerals
Tap water naturally contains various minerals. However, filtering it through reverse osmosis results in the removal of most these minerals. While this may not be a significant concern for all, those who depend on these minerals in their diet will need to compensate either by taking supplements or adjusting their dietary habits.
Alternatively, incorporating a remineralization filter into your RO system could be a solution. (To prevent adverse health effects, the WHO advises adding magnesium and calcium to low-mineral water to enhance its mineral content.)
Drawback: Potential for Significant Water Waste
Reverse osmosis can result in substantial water waste. This can be somewhat reduced by integrating a pressure pump or re-routing the wastewater through the system. However, it is impossible to eliminate wastewater production fully.
Remember that, despite this potential waste, reverse osmosis remains a more economically viable solution in the long run. The amount of water wasted depends on your specific system and setup. Although some designs are less wasteful than others, all will produce wastewater ranging from 0.2 gallons per gallon purified to 4 gallons of wastewater per gallon purified.
You could install a booster pump if your system generates a lot of wastewater. This should significantly improve the waste-to-purified water ratio. Make sure to check the wastewater specifications of the particular model when purchasing your product. Alternatively, provided it’s not excessively dirty, you can repurpose your wastewater for dishwashing and other cleaning activities.
Drawback: Maintenance Requirements
In general, maintaining a reverse osmosis system is relatively straightforward. Most importantly, you must replace the filters/membrane and occasionally clean the storage tank. The maintenance demanded by a reverse osmosis system is considerably less than that required by some other types of water filtration systems. However, neglecting maintenance could lead to problems.
Drawback: Slow Filtration Process
The reverse osmosis process is time-consuming. This is typically not a problem since most models come with a storage tank that stores pre-filtered water for immediate use. However, if you deplete all the water in your tank before it has a chance to refill, you could find yourself waiting several hours for the refill.
The system could also slow down if you do not change your pre-filters as scheduled or if debris clogs the RO membrane. Therefore, keeping up with maintenance tasks is vital.
Drawback: Space Requirements
Various types of reverse osmosis systems are available. Whole house systems require significant space, while the more common point-of-use systems require countertop space or room under your sink.
An average under-the-sink system requires at least 2×2 feet of space, including the storage tank. You might need more space for a larger or additional storage tank. You also need room in your sink to install the dedicated RO faucet. If under sink space is limited, installation in a nearby cabinet is an option.
Drawback: Separate Faucet Requirement
Your RO system connects not to your existing sink faucet but to its own specialized faucet. This might necessitate drilling an extra hole in your sink or utilizing the pre-drilled hole for your sink soap dispenser or spray hose.
It’s essential to use a faucet specifically designed for your reverse osmosis system. Using your regular tap would mean using RO water for all sink activities, which could be wasteful. Besides, RO water is delivered through its faucet at a slower flow rate than regular tap water, which isn’t suitable for your large, traditional faucet.
Drawback: Drain Line Necessity
RO systems must be connected to the drain pipe under your sink to dispose of the wastewater mentioned earlier. The downside is that you need to connect a wastewater saddle to your sink drain during installation and ensure it’s distanced from your dishwasher disposal. This can be somewhat tricky, particularly in limited spaces.
If you have any questions about reverse osmosis effectiveness please don’t hesitate to leave a comment below!
Information provided on BOS is for educational purposes only. The products and services we review may not be right for your individual circumstances.
We adhere to strict editorial guidelines. Rest assured, the opinions expressed have not been provided, reviewed, or otherwise endorsed by our partners – they are unbiased, independent, and the author’s alone. Our licensed experts fact-check all content for accuracy. It is accurate as of the date posted and to the best of our knowledge.