Question Answered: What Do Water Filter Pitchers Remove?
Written by: Gene Fitzgerald // Last Updated: Sep 7, 2023
This page may contain affiliate links. If you buy a product or service through such a link we earn a commission at no extra cost to you. Learn more.
When it comes to having clean and purified drinking water on a budget, water filter pitchers should be your go-to. They improve the taste and smell of your water and eliminate harmful contaminants too. On top of that, they are easy to use and much cheaper than bottled water.
Since all pitchers feature different technologies, there is no simple answer to what they can remove.
It’s true that most do a solid job at removing odors and tastes. Unfortunately, this is where it ends. Water filter pitchers often don’t feature powerful enough filtration to remove or reduce potentially hazardous chemicals, heavy metals and other organic/inorganic substances from your water.
In contrast, high-quality water filter pitchers like the Clearly Filtered are designed to remove hundreds of harmful contaminants, including lead, arsenic, BPA, chloramine, and PFAS.
Key Takeaways
- Not all water filter pitchers are created the same. They use different filtration methods to target different contaminants.
- Generally speaking, water filter pitchers can remove chlorine, chloramine, disinfection byproducts, lead, chromium 6, mercury and other heavy metals, pesticides, perfluorinated chemicals, pharmaceuticals, volatile organic compounds, fluoride, microplastic, bacteria, viruses, and more.
- Check a water filter pitcher for NSF/ANSI certifications as to what contaminants it can remove.
How Do Water Filter Pitchers Work?
Water filter pitchers are compact, nifty and easy-to-use filtration gadgets that feature a small filter cartridge right inside a jug. All you do is fill the pitcher with normal water from your tap and wait for a few minutes as the water passes through the cartridge. Clean water settles in the bottom reservoir, ready for drinking.
Although most filter pitchers look almost identical, the performance varies significantly between brands depending on the filter type. Of course, how well a pitcher water filter works also depends on your water quality.
Water Quality
Just like water quality varies from one place to another, filtration technologies also differ significantly. No pitcher water filter can remove all contaminants, and, therefore, you must understand your water chemistry before you make a purchase.
You can ask your local water utility for a detailed report about the level of contaminants in your water supply. Unfortunately, water quality is also affected by the distribution channels and the plumbing in your house. Hence, we advise getting a DIY water test kit or sending a sample to a certified laboratory for a comprehensive analysis.
Moreover, if you are using water from a public or private well, you should be more concerned about cysts, viruses, and bacteria – frequent dwellers of well water. On the other hand, you should look for chlorine and disinfection byproducts when using city/municipal water.
Filter Types
As mentioned, not all water filter pitchers are made alike. Different models use different filtration techniques to treat water. Here we discuss a few of the most common filter types used by different brands and what they remove.
Activated Carbon
Activated carbon is the most common medium for water filtration in water filter pitchers. In fact, almost all types of filtration processes – whether whole-house filters, reverse osmosis systems, shower filters or under-the-sink water filters etc. – mostly feature carbon-based technology in some way or the other.
But, all carbon filters are not designed in the same way either. Some perform way better than others, and some are designed to target a particular contaminant which others don’t.
Generally, the performance of an activated carbon filter relies on:
- The amount of carbon used which directly translates to the time it stays in contact with water
- The type of carbon used
- The purpose it was designed for
Activated carbon filters use carbon from any of these sources:
- Coconut shells (renewable and most commonly used)
- Wood-based coal (also referred to as activated charcoal)
- Bituminous coal
Some pitchers boast a granular activated carbon (GAC) filter, while others feature block carbon. A GAC filter has loose granules of carbon, while a block carbon is where powdered carbon is compressed and held together by a binding agent to form a filter.
How Do They Work?
Carbon filters work through adsorption. The carbon attracts contaminants, which are adsorbed or stuck onto the media surface. Undoubtedly, activated carbon filters are excellent at removing chlorine, bad taste and funky odor. However, modern carbon block filters can also remove other harmful elements like lead and asbestos.
That said, activated carbon filters are ineffective at removing certain contaminant groups like bacteria and viruses, salts and most heavy metals. These contaminants just sail right through the carbon as they don’t stick to the surface.
Fun Fact: Around 400 BC, Egyptians believed that keeping their water in a charcoal container made it taste better and purer. Thus, carbon filtration dates way back and has proved to be effective even then.
Ceramic Filters
Ceramic filters – some people also refer to them as candle filters – use natural ceramic filter media to process water. Most ceramic filters effectively remove even tiny contaminants like microorganisms through a network of pores. They are inexpensive, eco-friendly and effective at purifying your drinking water.
How Do They Work?
There are millions of pores on a ceramic filter cartridge. As water passes through the cartridge, the tiny pores block impurities.
One of the oldest types of water filtration systems on the market, ceramic filters replicate the Earth’s natural water purification process. Just like water from an aquifer makes its way through layers and layers of rocks to reach streams, the same way water penetrates through the natural ceramic medium to get rid of contaminants.
Quite often ceramic water filters are used in conjunction with other filter media inside water filter pitchers to achieve better filtration. Some are built with activated carbon, while others are treated with silver to decrease the chances of bacterial growth.
Ion Exchange Resin
Ion-exchange resin features spherical resin beads that attract oppositely charged atoms and molecules. It is an efficient method of removing many toxins from your drinking water.
Depending on the type of resin used, the ion exchange process can remove contaminants including:
- Nitrates
- Fluoride
- Iron
- Manganese
- Chromium
- Arsenic
- Radium, uranium
Note that in this case ion exchange in water filter pitchers has nothing to do with water softening. While water softeners also use ion-exchange technology, they are entirely different appliances designed to remove excess hardness minerals.
What Do Water Filter Pitchers Remove?
Here is a long list of contaminants a water filter pitcher can remove if it’s good. Please keep in mind that this list does not apply to all brands and models. You must look for NSF certifications to ensure which pitcher is certified to reduce which contaminant and to what percentage.
Chlorine
Chlorine is not essentially a “contaminant”. Instead, it is a disinfection chemical added at the water utility to prevent the growth of microorganisms that exist in surface waters and groundwater.
Chlorination is just one of the many methods to disinfect water. And since it is one of the easiest to eliminate pathogens rapidly, it’s been used for over a century.
You may ask, why remove something that was deliberately added to our water in the first place? This is because chlorine stays in your water and make it taste and smell bad – the most common complaint with tap water.
Besides, as we will discuss further, it interacts with organic substances in the water and produces harmful byproducts, also called DBPs.
So, if you don’t like the taste of chlorinated water but also don’t want to drink water that is chock full of harmful chemicals, you’d be glad to know most water filter pitchers do an excellent job at removing chlorine.
In a nutshell, pitcher water filters that feature activated carbon filtration are great at eliminating chlorine, making your water crisp and tasty. Be sure to look for an NSF standard 42 certification that tests a filter for its chlorine removing properties.
Chloramine
Many utilities in the US are now using chloramine instead of chlorine to disinfect their water. This is because chloramine is far more stable than chlorine and does not react that strongly with organic substances.
Unfortunately, chloramines pose a high risk for hemodialysis patients. They are also responsible for nitrosamines, a new type of disinfection byproduct. The worst news is nitrosamines are strongly associated with cancer.
The process of removing chloramine is far more complex than removing chlorine. This is where catalytic carbon comes into play, which is by far the most effective form of filtration for chloramines.
Some water filter pitchers also claim to remove chloramine from your water using activated carbon, but these claims aren’t valid. This is because chloramine removal is not possible through regular activated carbon in a filter pitcher. Granted, these pitchers might reduce the level of chloramines slightly, but that’s about it.
Disinfection Byproducts (DBPs)
Disinfection byproducts are produced due to the chemical treatment of water for removing microbial components and prevention of water-borne diseases. There are many different types of harmful DBPs that can be lurking around in water, depending on the primary disinfectant. For example:
- Trihalomethanes (THMs)
- Haloacetic acetic acids (HAAs)
- Chlorite
- Chlorate
- Organic chloramines
Long-term consumption of DPBs present in chlorinated water has been associated with an increased risk of bladder cancer. But not to worry, any basic water filter pitcher using activated carbon is perfectly suited for removing disinfection byproducts.
Lead
Lead can occur naturally in your water supply or enter your water due to the corrosion of pipes and other plumbing components.
Since you can’t see or smell lead, you would never know it exists in your water. The EPA has set the maximum contaminant level for lead to be zero because even a tiny amount can be lethal.
So it means most of your tap water is already treated for lead at the source. Unfortunately, once the water leaves the treatment plant, it can pick up lead from the distribution channels or your own plumbing.
If your house was made before 1986 (the year lead pipes were banned) you are more likely to be facing this contaminant, which is alarming since lead poisoning is extremely harmful, especially for growing kids. Over time lead can accumulate in your body and cause:
- Hearing loss
- Anemia
- Hypertension
- Immune system dysfunction
- Reduced sperm count
- Mood disorders
- Miscarriage, stillbirth or premature birth
Which type of water filter pitcher do you need in order to get rid of lead? We recommend ion exchange, solid activated carbon and ceramic.
Chromium 6
Chromium 6 is a known carcinogen and a reproductive toxicant for males and females alike. Chromium 6 exposure through drinking water can also cause:
- Liver and kidney damage
- Diarrhea
- Stomach and intestinal bleeding
- Cramps
Clearly Filtered and ZeroWater filter pitchers both do a good job at removing chromium 6 using ion exchange.
Mercury & Other Heavy Metals
Mercury is formed by the natural degassing of the Earth’s surface. The EPA found out that the presence of mercury and other heavy metals can cause potential damage to the kidneys, brain and developing fetuses. It can also affect brain functioning, leading to irritability and memory problems.
Most GAC filters can effectively reduce the level of mercury in drinking water. Ion exchange and KDF filter media work even better.
Pesticides
Pesticides including herbicides trickle into the ground and find their way to aquifers from farming fields, accidental spills and improper disposal.
When pesticides are found in water, they are not high enough to cause acute illnesses. Nevertheless, they degrade the quality of water making it unsafe to drink.
Water filter pitchers using activated carbon are found to be effective at removing pesticides from water.
Perfluorinated Chemicals
Perfluorinated chemicals are man-made chemicals that have been widely used in a variety of products. They are now being found in our water and soil. And they are becoming an increasing concern for people since they can reduce immune functionality and cause problems for the liver and pancreas.
Catalytic carbon and ion exchange are the best defense against PFOS. Our recommended water filter pitcher: The Clearly Filtered.
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical contaminants in water include:
- Personal care products
- Wastewater compounds
- Antibiotics
- Animal and human hormones
- Detergents
- Antimicrobials
Nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and activated carbon have proven to rid your drinking water from these pharmaceutical wastes.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
VOCs refer to several harmful contaminants that can cause a variety of symptoms:
- Eye, nose and throat irritation
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Skin related issues
A higher level of VOCs can also cause problems with the liver, kidney and nervous system. Long-term exposure to VOCs, even at low concentrations, is also linked with cancer.
Most carbon-based pitcher water filters can effectively remove VOCs from drinking water.
Fluoride
Fluoride is added by public water systems at about 0.7 milligram per liter (0.7 mg/L) to help prevent tooth decay. But since fluoride is a natural element already present in soils, the water may have more than a safe amount of fluoride.
If children under nine years of age are exposed to a higher level, i.e., 2 mg/L, it can lead to mottling, a discoloration of permanent teeth.
If the levels are above 4 mg/L, it can lead to severe crippling skeletal fluorosis. This is a painful condition where the bones become brittle, similar to osteoporosis.
The best way to remove fluoride using a water filter pitcher is through ion exchange.
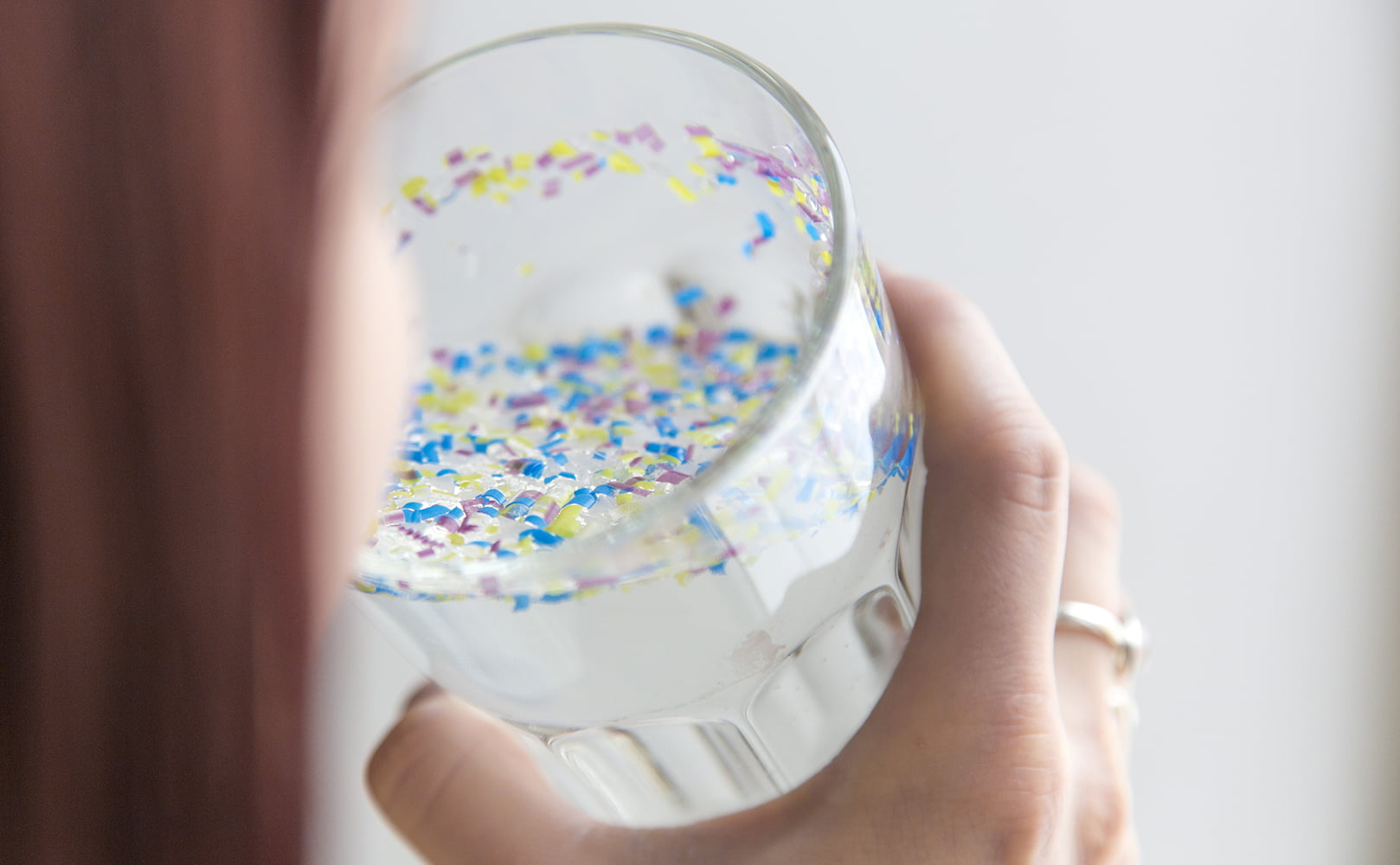
Microplastic
For decades, microplastics have slowly made their way into our drinking water. A recent study analyzed drinking water samples and found that each liter of water contains on average 4.34 plastic particles.
Long term consumption of water high in microplastics can cause:
- Toxicity
- Inflammatory lesions
- Metabolic disturbances
- Increased risk of cancer
Unfortunately, most water filter pitchers cannot remove microplastics since they are so small. Ceramic filters provide the best chance of removal.
Bacteria & Viruses
Bacteria and viruses are organic contaminants that may either be harmless, harmful or beneficial. Some of the most dangerous microbial contaminants in drinking water are E Coli, Giardia and Cryptosporidium, which can cause flu-like symptoms or weaken the gut.
Some ceramic pitcher water filters can effectively remove bacteria and viruses.
NSF Certifications
NSF International is a public health agency that develops standards for products like water filters. If a water filter has been certified according to NSF standards, it’s independently tested and approved to do exactly what is advertised. This could mean that it reduces one or more contaminants below a certain level or that the production materials are free from harmful stuff such as lead.
By the way, one product can have more than one NSF certification. Here are the most common ones related to pitcher water filtration systems.
NSF/ANSI Standard 42
Standard 42 measures the ability of a water filter pitcher to remove contaminants that alter water aesthetics. Thus, it focuses on chlorine and large particulates.
NSF/ANSI Standard 53
Also known as the “health effects standard”, NSF standard 53 certifies that a filter pitcher can reduce contaminants with a health effect. Be careful, though, a certification does not imply that a water filter pitcher removes all harmful contaminants, but only those it was successfully tested for.
NSF/ANSI Standard 244
Filters that provide microbiologically-safe water and are thus allowed to be used for public water supplies and private wells are awarded this certification.
NSF/ANSI Standard 401
For filter pitchers that remove one or more out of the 15 emerging contaminants like prescription drugs, OTC medicines and pesticides.
NSF/ANSI Protocol 473
This protocol highlights the requirements for a water filter pitcher that removes PFOS and PFOAs (the forever chemicals).
If you have any questions about what contaminants do water filter pitchers remove please don’t hesitate to leave a comment below!
Information provided on BOS is for educational purposes only. The products and services we review may not be right for your individual circumstances.
We adhere to strict editorial guidelines. Rest assured, the opinions expressed have not been provided, reviewed, or otherwise endorsed by our partners – they are unbiased, independent, and the author’s alone. Our licensed experts fact-check all content for accuracy. It is accurate as of the date posted and to the best of our knowledge.